When you create a complete competency structure you must first create the elements that make up the structure and associate these elements together. Associated elements have a parent-child relationship. For example, if an activity is associated with a learning objective, the activity is the child and the learning objective is the parent.
You can create the following element associations:
| Element | Parents | Children |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Other competencies |
Learning objectives Other competencies |
|
|
Competencies Other learning objectives |
Activities Other learning objectives |
|
|
Learning objectives |
Tip If you want to create more complex structures (e.g. a learning objective associated with two competencies in different levels of a nested structure), consider creating all of your elements first before adding parent-child relationships.
The Structure Summary page of an element you select displays all parent and children elements associated with it. If a competency or learning objective is available in multiple org units, you can only see the current org unit's associated activities in the structure.
You can nest competencies and learning objectives by adding a parent-child association between competencies or between learning objectives.
If you have one learning objective that is very broad in scope, dividing it into simpler learning objectives and nesting them beneath it allows users to complete the learning objective in smaller parts. This might also provide a more detailed view of the experiences involved to achieve the overall learning objective.
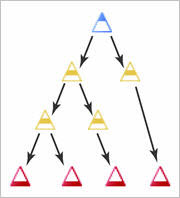
An example of nested learning objectives in a competency structure
Nested competencies are ideal if competencies are prerequisites for achieving an overarching competency. For example, if you want to distinguish multiple levels of proficiency, a user might complete a "Basic" level profiency competency by achieving two learning objectives, then complete an "Intermediate" level proficiency competency by completing two more learning objectives.
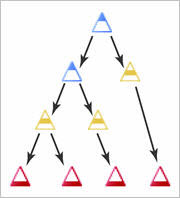
An example of nested competencies in a competency structure
Note If users can view competencies, nested competencies are displayed individually and also within their parent-child associations.
Separate competency structures in the same org unit overlap if they contain the same competencies, learning objectives, or activities. This is ideal for elements that are relevant to completing multiple competency structures.
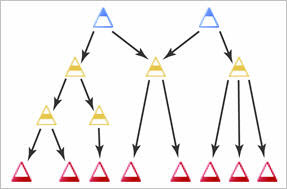
An example of overlapping competency structures